Celltrion’s Strategy for ADC Therapeutics
2025.05.14
Antibody therapeutics have become a key treatment representing the biopharmaceutical market due to their advantages of better treatment effects and fewer side effects than chemical drugs. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are rapidly emerging as one of the most promising modalities in oncology. Building on the global prominence of monoclonal antibody therapies as a cornerstone of the biopharmaceutical market, ADCs represent a next-generation treatment approach that combines the targeting ability of monoclonal antibodies with the potency of cytotoxic drugs. By linking these two elements, ADCs are designed to deliver powerful anti-cancer agents directly to tumor cells—maximizing efficacy while minimizing harm to healthy tissue.
ADCs typically consist of four key components: an antibody that targets diseased cells, a highly potent drug (payload), a linker that connects the two, and a surface antigen that directs the antibody to its target. These elements must work in close coordination to ensure precise targeting, strong therapeutic effects, and patient safety.
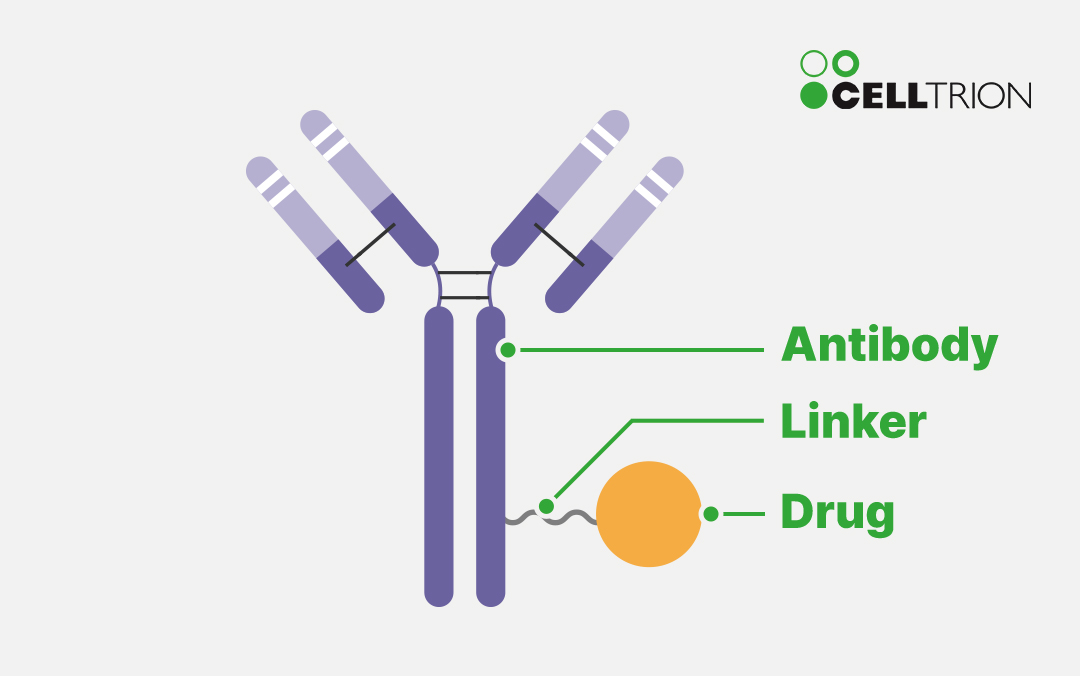
Despite their potential, ADCs present several technical challenges. To achieve effective drug delivery to tumor sites, each component of the ADC must be precisely optimized—this includes using highly potent payloads, engineering antibodies with high affinity for target antigens, and designing linkers that remain stable in circulation but reliably release the drug inside cancer cells.
Linker technology plays a particularly important role. Cleavable linkers break apart in response to conditions such as acidity or enzymatic activity within tumor cells. Non-cleavable linkers, by contrast, release the payload only after the antibody is fully degraded. Choosing the right linker type is essential to balancing efficacy and safety.
Celltrion is actively advancing its ADC pipeline by combining its deep antibody engineering expertise with innovative linker and payload platforms. The company is developing oncology-focused ADC candidates and preparing for global clinical trials. Its development strategy prioritizes not only therapeutic efficacy and targeting accuracy, but also drug delivery stability and long-term treatment durability.
A key area of focus is the development of bispecific ADCs, which are capable of binding to two distinct antigens on cancer cells instead of just one. This enhances target specificity and improves therapeutic outcomes. Celltrion is also applying advanced antibody modification techniques—such as peptide masking and Fc silencing—to reduce off-target effects and increase safety.
In parallel, the company is exploring dual-payload ADCs that combine two different cytotoxic agents. For example, a topoisomerase inhibitor may be paired with a microtubule inhibitor to disrupt both DNA replication and cell division. Some of these combinations are being evaluated with DDR (DNA damage response) inhibitors, which block cancer cell repair mechanisms. This multi-pronged approach aims to enhance efficacy even at lower dosages, while reducing side effects and improving tolerability.
With its accumulated expertise in antibody design and drug delivery platforms, Celltrion is strategically expanding its presence in the ADC field. By focusing on precision, safety, and continuous innovation, the company aims to deliver next-generation oncology treatments that create new value in the global biopharmaceutical landscape.